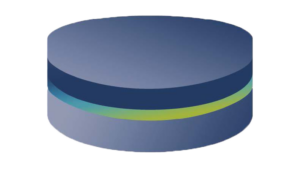
An SOI wafer typically consists of three main layers:
Device Layer:
The top layer of the SOI wafer consists of a thin layer of high-purity silicon that serves as the active area for the manufacture of semiconductor devices. This silicon layer can normally have thicknesses ranging from a few nanometers to a few micrometers, depending on the requirements of the application.
Buried Thermal Oxide (BOX):
Underneath the active silicon layer is an insulating layer, usually made of silicon dioxide (SiO2). This insulating layer separates the active silicon layer from the underlying substrate and prevents electrical interactions and leakage currents between the layers.
Handle wafer:
The lowest substrate of the SOI wafer consists of a silicon substrate that serves as a mechanical support and structural base for the thin layers. The carrier substrate can usually have a standard silicon wafer structure.